Further Evidence That Cannabis Moderates Familial Correlation of Psychosis-Related Experiences

Published: September 18, 2015
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137625
Ruud van Winkel – University Psychiatric Center KU, Leuven, Belgium
Abstract
Background
Familial correlations underlie heritability estimates of psychosis. If gene-environment interactions are important, familial correlation will vary as a function of environmental exposure.
Methods
Associations between sibling and parental schizotypy (n = 669 pairs, n = 1222 observations), and between sibling schizotypy and patient CAPE psychosis (n = 978 pairs, n = 1723 observations) were examined as a function of sibling cannabis use. This design is based on the prediction that in unaffected siblings who are not exposed, vulnerability for psychosis will remain latent, whereas in case of exposure, latent psychosis vulnerability may become expressed, at the level of schizotypal symptoms, causing the phenotypic correlation between relatives to become “visible” under the influence of cannabis.
Results
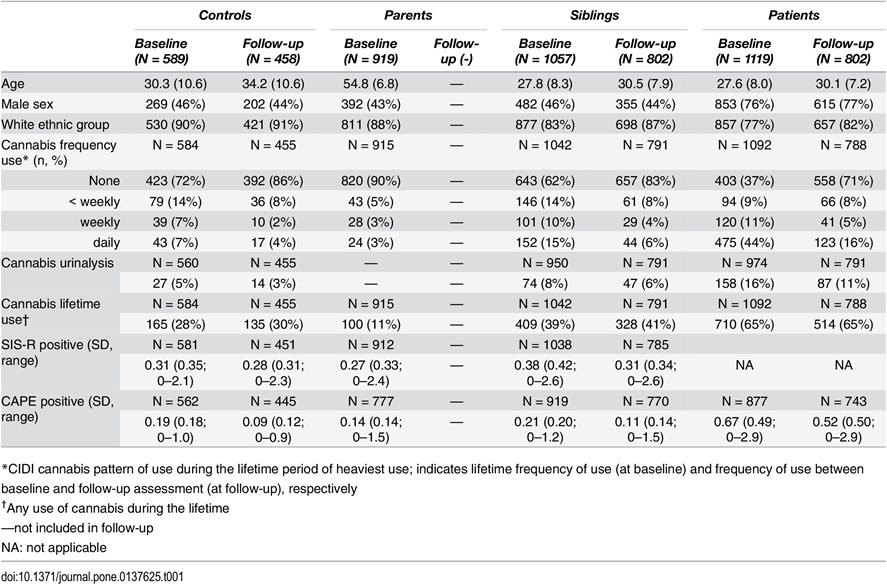
Siblings exposed to recent cannabis use resembled their patient-relative more closely in terms of positive schizotypy (urinalysis(+):B = 0.30, P<.001; urinalysis(-):B = 0.10, p<0.001; p-interaction = 0.0135). Similarly, the familial correlation in positive schizotypy between parent and sibling was significantly greater in siblings recently exposed to cannabis (urinalysis(+):B = 0.78, P<.001; urinalysis(-):B = 0.43, p<0.001; p interaction = 0.0017). Results were comparable when using lifetime cannabis frequency of use as exposure instead of recent use. Parental schizotypy did not predict cannabis use in the healthy sibling, nor in the patient. Similarly, parental cannabis use was not associated with level of schizotypy in the sibling, nor with psychotic symptoms in the patient, making gene-environment correlation unlikely.
Conclusion
Familial correlation of psychosis-related experiences varies considerably as a function of exposure to cannabis, confirming the importance of gene-cannabis interaction in shifts of expression of psychosis-related experiences
http://www.plosone.org/article/Authors/info:doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0137625


